CF896C-Willem, Chtholly and Seniorious
题目:
题目描述:
— Willem…
— What’s the matter?
— It seems that there’s something wrong with Seniorious…
— I’ll have a look…

Seniorious is made by linking special talismans in particular order.
After over 500 years, the carillon is now in bad condition, so Willem decides to examine it thoroughly.
Seniorious has $ n $ pieces of talisman. Willem puts them in a line, the $ i $ -th of which is an integer $ a_{i} $ .
In order to maintain it, Willem needs to perform $ m $ operations.
There are four types of operations:
- $ 1\ l\ r\ x $ : For each $ i $ such that $ l<=i<=r $ , assign $ a_{i}+x $ to $ a_{i} $ .
- $ 2\ l\ r\ x $ : For each $ i $ such that $ l<=i<=r $ , assign $ x $ to $ a_{i} $ .
- $ 3\ l\ r\ x $ : Print the $ x $ -th smallest number in the index range $ [l,r] $ , i.e. the element at the $ x $ -th position if all the elements $ a_{i} $ such that $ l<=i<=r $ are taken and sorted into an array of non-decreasing integers. It’s guaranteed that $ 1<=x<=r-l+1 $ .
- $ 4\ l\ r\ x\ y $ : Print the sum of the $ x $ -th power of $ a_{i} $ such that $ l<=i<=r $ , modulo $ y $ , i.e.
 .
.
输入格式:
The only line contains four integers $ n,m,seed,v_{max} $ ( $ 1<=n,m<=10^{5},0<=seed<10^{9}+7,1<=vmax<=10^{9} $ ).
The initial values and operations are generated using following pseudo code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| def rnd():
ret = seed
seed = (seed * 7 + 13) mod 1000000007
return ret
for i = 1 to n:
a[i] = (rnd() mod vmax) + 1
for i = 1 to m:
op = (rnd() mod 4) + 1
l = (rnd() mod n) + 1
r = (rnd() mod n) + 1
if (l > r):
swap(l, r)
if (op == 3):
x = (rnd() mod (r - l + 1)) + 1
else:
x = (rnd() mod vmax) + 1
if (op == 4):
y = (rnd() mod vmax) + 1
|
Here $ op $ is the type of the operation mentioned in the legend.
输出格式:
For each operation of types $ 3 $ or $ 4 $ , output a line containing the answer.
样例:
样例输入 1:
样例输出 1:
样例输入 2:
样例输出 2:
思路:
实现:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
| #include "ybwhead/ios.h"
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int maxn = 1e5 + 7;
long long ksm(long long a, long long b, long long mod)
{
long long res = 1;
long long ans = a % mod;
while (b)
{
if (b & 1)
res = res * ans % mod;
ans = ans * ans % mod;
b >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
struct node
{
int l, r;
mutable long long v;
node(int L, int R = -1, long long V = 0) : l(L), r(R), v(V) {}
bool operator<(const node &o) const
{
return l < o.l;
}
};
typedef set<node>::iterator IT;
set<node> s;
IT split(int pos)
{
IT it = s.lower_bound(node(pos));
if (it != s.end() && it->l == pos)
return it;
--it;
int L = it->l, R = it->r;
long long V = it->v;
s.erase(it);
s.insert(node(L, pos - 1, V));
return s.insert(node(pos, R, V)).first;
}
void add(int l, int r, long long val = 1)
{
IT itl = split(l), itr = split(r + 1);
for (; itl != itr; ++itl)
itl->v += val;
}
void assign_val(int l, int r, long long val = 0)
{
IT itl = split(l), itr = split(r + 1);
s.erase(itl, itr);
s.insert(node(l, r, val));
}
long long rnk(int l, int r, int k)
{
vector<pair<long long, int>> vp;
IT itl = split(l), itr = split(r + 1);
vp.clear();
for (; itl != itr; ++itl)
vp.push_back(pair<long long, int>(itl->v, itl->r - itl->l + 1));
std::sort(vp.begin(), vp.end());
for (vector<pair<long long, int>>::iterator it = vp.begin(); it != vp.end(); ++it)
{
k -= it->second;
if (k <= 0)
return it->first;
}
return -1;
}
long long sum(int l, int r, int ex, int mod)
{
IT itl = split(l), itr = split(r + 1);
long long res = 0;
for (; itl != itr; ++itl)
res = (res + (long long)(itl->r - itl->l + 1) * ksm(itl->v, (ex), (mod))) % mod;
return res;
}
int n, m;
long long seed, vmax;
long long rnd()
{
long long ret = seed;
seed = (seed * 7 + 13) % mod;
return ret;
}
long long a[maxn];
int main()
{
yin >> n >> m >> seed >> vmax;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
{
a[i] = (rnd() % vmax) + 1;
s.insert(node(i, i, a[i]));
}
s.insert(node(n + 1, n + 1, 0));
int lines = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i)
{
int op = int(rnd() % 4) + 1;
int l = int(rnd() % n) + 1;
int r = int(rnd() % n) + 1;
if (l > r)
std::swap(l, r);
int x, y;
if (op == 3)
x = int(rnd() % (r - l + 1)) + 1;
else
x = int(rnd() % vmax) + 1;
if (op == 4)
y = int(rnd() % vmax) + 1;
if (op == 1)
add(l, r, (x));
else if (op == 2)
assign_val(l, r, (x));
else if (op == 3)
yout << rnk(l, r, x) << endl;
else
yout << sum(l, r, x, y) << endl;
}
return 0;
}
|

 .
.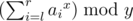 .
.