题目:
题目描述:
In one well-known algorithm of finding the $ k $ -th order statistics we should divide all elements into groups of five consecutive elements and find the median of each five. A median is called the middle element of a sorted array (it’s the third largest element for a group of five). To increase the algorithm’s performance speed on a modern video card, you should be able to find a sum of medians in each five of the array.
A sum of medians of a sorted $ k $ -element set $ S={a_{1},a_{2},…,a_{k}} $ , where $ a_{1}<a_{2}<a_{3}<…<a_{k} $ , will be understood by as
 The
The  operator stands for taking the remainder, that is
operator stands for taking the remainder, that is  stands for the remainder of dividing $ x $ by $ y $ .
stands for the remainder of dividing $ x $ by $ y $ .
To organize exercise testing quickly calculating the sum of medians for a changing set was needed.
输入格式:
The first line contains number $ n $ ( $ 1<=n<=10^{5} $ ), the number of operations performed.
Then each of $ n $ lines contains the description of one of the three operations:
- add $ x $ — add the element $ x $ to the set;
- del $ x $ — delete the element $ x $ from the set;
- sum — find the sum of medians of the set.
For any add $ x $ operation it is true that the element $ x $ is not included in the set directly before the operation.
For any del $ x $ operation it is true that the element $ x $ is included in the set directly before the operation.
All the numbers in the input are positive integers, not exceeding $ 10^{9} $ .
输出格式:
For each operation sum print on the single line the sum of medians of the current set. If the set is empty, print 0.
Please, do not use the %lld specificator to read or write 64-bit integers in C++. It is preferred to use the cin, cout streams (also you may use the %I64d specificator).
样例:
样例输入1:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| 6
add 4
add 5
add 1
add 2
add 3
sum
|
样例输出1:
样例输入2:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| 14
add 1
add 7
add 2
add 5
sum
add 6
add 8
add 9
add 3
add 4
add 10
sum
del 1
sum
|
样例输出2:
思路:
实现:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
| // Problem: CF85D Sum of Medians
// Contest: Luogu
// URL: https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/CF85D
// Memory Limit: 250 MB
// Time Limit: 3000 ms
// Author: Ybw051114
//
// Powered by CP Editor (https://cpeditor.org)
#include "ybwhead/ios.h"
using namespace std;
#define int long long
const int QU = 100000, A_I = 1000000000, LOG_A_I = 30;
int qu; //操作数
struct segtree
{ //动态开点线段树
int sz; //点数
struct node
{
int l, r, lson, rson, sum[5], cnt;
} nd[QU * LOG_A_I + 1];
#define l(p) nd[p].l
#define r(p) nd[p].r
#define lson(p) nd[p].lson
#define rson(p) nd[p].rson
#define sum(p) nd[p].sum
#define cnt(p) nd[p].cnt
int nwnd(int l = 1, int r = A_I)
{
return nd[++sz] = node({l, r, 0, 0, {0, 0, 0, 0, 0}, 0}), sz;
} //新建节点
void init()
{
nd[0] = node({0, 0, 0, 0, {0, 0, 0, 0, 0}, 0});
sz = 0;
nwnd();
} //线段树初始化
void sprup(int p)
{ //上传
cnt(p) = cnt(lson(p)) + cnt(rson(p));
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
sum(p)[i] = sum(lson(p))[i] + sum(rson(p))[(((i - cnt(lson(p))) % 5) + 5) % 5];
}
void add(int x, int p = 1)
{ //add操作
if (l(p) == r(p))
return sum(p)[1] = x, cnt(p) = 1 /*此数in s*/, void();
int mid = l(p) + r(p) >> 1;
if (x <= mid)
add(x, lson(p) = lson(p) ? lson(p) : nwnd(l(p), mid));
else
add(x, rson(p) = rson(p) ? rson(p) : nwnd(mid + 1, r(p)));
sprup(p);
}
void del(int x, int p = 1)
{ //del操作
if (l(p) == r(p))
return sum(p)[1] = cnt(p) = 0 /*此数notin s*/, void();
int mid = l(p) + r(p) >> 1;
if (x <= mid)
del(x, lson(p) = lson(p) ? lson(p) : nwnd(l(p), mid));
else
del(x, rson(p) = rson(p) ? rson(p) : nwnd(mid + 1, r(p)));
sprup(p);
}
int _sum() /*sum操作*/ { return sum(1)[3]; }
} segt;
signed main()
{
yin >> qu;
segt.init(); //线段树初始化
while (qu--)
{
string tp;
int x;
yin >> tp;
if (tp == "add")
yin >> x, segt.add(x);
else if (tp == "del")
yin >> x, segt.del(x);
else
yout << segt._sum() << "\n";
}
return 0;
}
|
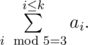 The
The 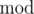 operator stands for taking the remainder, that is
operator stands for taking the remainder, that is 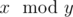 stands for the remainder of dividing $ x $ by $ y $ .
stands for the remainder of dividing $ x $ by $ y $ .